On the current status of nuclear power generation, such as advantages and disadvantages introduced by allsinfo 원자력 발전 장점과 단점 등 현황에 대하여
안녕하세요 세상 모든 유용한 지식 그 무엇이든을 연재 중인 allsinfo에요 오늘 준비한 내용은 대한민국이 선택할 수 있는 가장 현실적이고 경제적이며 유용할 수 있는 에너지원인 원자력을 활용한 발전방식인 원자력 발전 장점과 그 단점 등 알아두면 유용할 내용까지 최대한 간단히 그리고 핵심만 설명할게요.
도움 되길 바라며 시작합니다.

원자력 발전: 지속 가능한 미래를 위한 선택
원자력 발전은 우리 사회에서 뜨거운 논쟁의 대상이 되고 있습니다. 일부는 원자력 발전이 환경 친화적이고 지속 가능한 에너지원이라고 주장하지만, 다른 이들은 안전성과 방사능 폐기물 처리에 대한 우려를 제기합니다. 이 글에서는 원자력 발전의 장단점을 균형 잡힌 시각으로 살펴보고, 그 역할과 미래에 대해 깊이 있게 탐구해 보고자 합니다.
1. 원자력 발전의 장점
1.1. 탄소 배출 감소와 기후 변화 대응
원자력 발전은 화석 연료 발전에 비해 온실가스 배출이 매우 적어 기후 변화 대응에 기여할 수 있습니다. 이는 지속 가능한 에너지 공급을 위한 중요한 해결책으로 주목받고 있습니다.
1.2. 안정적인 전력 공급
원자력 발전은 연료 공급의 안정성이 높아 전력 공급의 안정성을 보장합니다. 이는 산업 발전과 국가 경제에 필수적인 요소입니다.
1.3. 경제성
원자력 발전은 장기적으로 볼 때 화석 연료 발전에 비해 경제성이 높은 것으로 평가됩니다. 초기 건설 비용은 높지만, 운영 및 연료 비용이 저렴해 전력 생산 단가가 낮습니다.
2. 원자력 발전의 단점
2.1. 방사능 폐기물 처리
원자력 발전 과정에서 발생하는 방사능 폐기물은 장기간 안전하게 관리해야 하는 문제가 있습니다. 이에 대한 해결책 마련이 시급한 과제입니다.
2.2. 안전성 우려
원자력 발전소 사고의 위험성과 잠재적인 피해로 인해 안전성에 대한 우려가 높습니다. 철저한 안전 관리 체계 구축이 필요합니다.
2.3. 공공 수용성 저하
원자력 발전에 대한 부정적 인식이 확산되면서 공공의 수용성이 낮아지고 있습니다. 이를 극복하기 위한 노력이 요구됩니다.
3. 원자력 발전의 미래
3.1. 기술 혁신과 안전성 강화
최근 소형 모듈형 원자로, 4세대 원자로 등 새로운 원자력 기술이 개발되고 있습니다. 이를 통해 안전성과 경제성이 크게 향상될 것으로 기대됩니다.
3.2. 방사능 폐기물 관리 기술 발전
심지층 처분, 핵연료 재활용 등 방사능 폐기물 관리 기술이 지속적으로 발전하고 있습니다. 이를 통해 폐기물 문제 해결의 실마리를 찾을 수 있을 것으로 보입니다.
3.3. 공공 수용성 제고 노력
정부와 산업계는 원자력 발전의 안전성과 필요성을 적극적으로 알리고, 주민 참여형 의사결정 체계를 구축하는 등 공공 수용성 제고를 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
3.4. 원자력 발전의 역할 재정립
기술 발전과 사회적 합의를 바탕으로 원자력 발전의 역할이 재정립될 것으로 전망됩니다. 탄소 중립 달성을 위한 주요 수단으로 자리 잡을 수 있을 것입니다.
결론
원자력 발전은 지속 가능한 미래를 위한 중요한 선택지 중 하나입니다. 기술 혁신과 사회적 합의를 통해 안전성과 공공 수용성을 높이고, 방사능 폐기물 관리 문제를 해결한다면 원자력 발전은 탄소 중립 달성을 위한 핵심 수단이 될 것입니다. 이를 위해 정부, 산업계, 시민사회가 함께 노력해 나가야 할 것입니다.
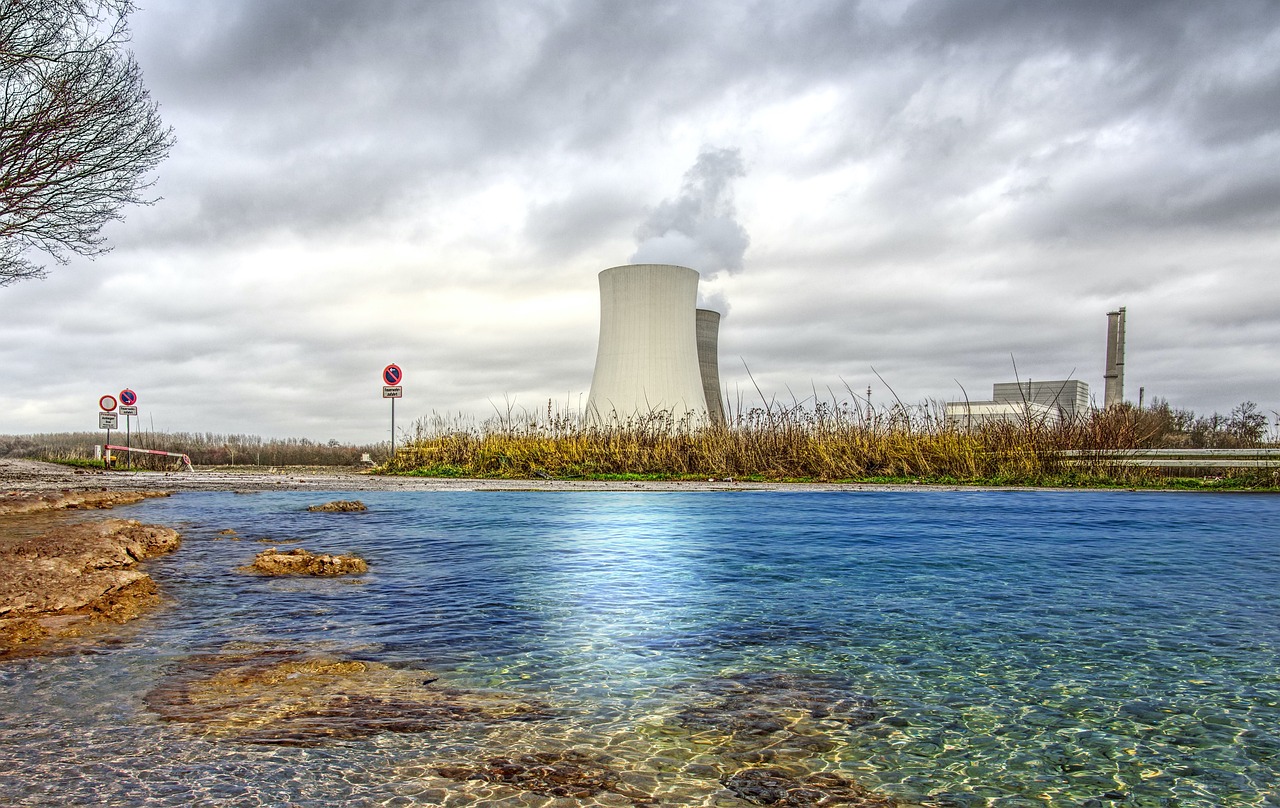






3. 원자력 발전의 미래
3.1. 기술 혁신과 안전성 강화
최근 소형 모듈형 원자로, 4세대 원자로 등 새로운 원자력 기술이 개발되고 있습니다. 이를 통해 안전성과 경제성이 크게 향상될 것으로 기대됩니다.
3.2. 방사능 폐기물 관리 기술 발전
심지층 처분, 핵연료 재활용 등 방사능 폐기물 관리 기술이 지속적으로 발전하고 있습니다. 이를 통해 폐기물 문제 해결의 실마리를 찾을 수 있을 것으로 보입니다.
3.3. 공공 수용성 제고 노력
정부와 산업계는 원자력 발전의 안전성과 필요성을 적극적으로 알리고, 주민 참여형 의사결정 체계를 구축하는 등 공공 수용성 제고를 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
3.4. 원자력 발전의 역할 재정립
기술 발전과 사회적 합의를 바탕으로 원자력 발전의 역할이 재정립될 것으로 전망됩니다. 탄소 중립 달성을 위한 주요 수단으로 자리잡을 수 있을 것입니다.
결론
원자력 발전은 지속 가능한 미래를 위한 중요한 선택지 중 하나입니다. 기술 혁신과 사회적 합의를 통해 안전성과 공공 수용성을 높이고, 방사능 폐기물 관리 문제를 해결한다면 원자력 발전은 탄소 중립 달성을 위한 핵심 수단이 될 것입니다. 이를 위해 정부, 산업계, 시민사회가 함께 노력해 나가야 할 것입니다.
5. 결론
원자력 발전은 기술 혁신과 사회적 합의를 통해 지속 가능한 미래 에너지원으로 자리잡을 수 있을 것입니다.
첫째, 새로운 원자로 기술 개발과 안전성 강화로 원자력 발전의 경제성과 안전성이 크게 향상될 것으로 기대됩니다. 또한 방사능 폐기물 관리 기술의 발전으로 이 문제에 대한 해결책을 찾을 수 있을 것입니다.
둘째, 정부와 산업계의 적극적인 노력으로 원자력 발전의 필요성과 안전성에 대한 국민 이해와 공공 수용성이 제고될 것입니다. 주민 참여형 의사결정 체계 구축 등을 통해 사회적 합의를 이뤄나갈 수 있을 것입니다.
셋째, 이러한 기술적, 사회적 진전을 바탕으로 원자력 발전의 역할이 재정립될 것입니다. 탄소 중립 달성을 위한 핵심 수단으로 자리 잡아, 지속 가능한 미래를 실현하는 데 기여할 수 있을 것입니다.
이를 위해서는 정부, 산업계, 시민사회가 함께 노력해야 할 것입니다. 원자력 발전의 안전성과 필요성에 대한 사회적 합의를 바탕으로, 기술 혁신과 제도 개선을 지속적으로 추진해 나가야 할 것입니다.
국내 발전 현황은?
원전 보유 현황:
- 한국은 세계 6위의 원자력 발전 국가로, 24기의 원전을 운영하고 있습니다.
- 총 발전량의 약 30%를 원자력 발전으로 충당하고 있습니다.
정부의 정책 방향:
- 정부는 2050년 탄소 중립 목표 달성을 위해 원자력 발전 비중을 확대할 계획입니다.
- 차세대 원자로 개발과 안전성 강화에 힘쓰고 있습니다.
기술 개발 및 안전성 강화:
- 소형 모듈형 원자로, 4세대 원자로 등 새로운 원자력 기술이 개발되고 있습니다.
- 이를 통해 안전성과 경제성이 크게 향상될 것으로 기대됩니다.
방사성 폐기물 관리:
- 심지층 처분, 핵연료 재활용 등 방사성 폐기물 관리 기술이 발전하고 있습니다.
- 이를 통해 폐기물 문제 해결의 실마리를 찾을 수 있을 것으로 보입니다.
공공 수용성 제고:
- 정부와 산업계는 원자력 발전의 안전성과 필요성을 적극적으로 알리고 있습니다.
- 주민 참여형 의사결정 체계 구축 등을 통해 공공 수용성 제고를 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
요약하면, 한국은 원자력 발전을 탄소 중립 달성을 위한 주요 수단으로 활용할 계획이며, 기술 혁신과 사회적 합의 제고를 통해 원자력 발전의 지속 가능성을 높이고자 노력하고 있습니다.
원자력 발전소 개소
현재 한국에는 총 24기의 원자력 발전소가 운영되고 있습니다 이 24기의 원자력 발전소는 다음과 같은 6개 발전소 부지에 위치하고 있습니다:
- 고리 원자력 발전소 (부산)
- 한빛 원자력 발전소 (전남 영광)
- 한울 원자력 발전소 (경북 울진)
- 월성 원자력 발전소 (경북 경주)
- 한국원자력연구원 (대전)
- 신고리 원자력 발전소 (부산)
이 중 고리, 한빛, 한울, 월성 원전이 주요 원자력 발전소 부지입니다. 또한 최근에는 신고리 원전이 추가로 건설되어 운영되고 있습니다.
따라서 현재 한국에는 총 6개의 원자력 발전소 부지에서 24기의 원자력 발전소가 가동 중이라고 볼 수 있습니다.
이렇게 준비한 내용은 끝이 났고 작성자는 올스인포였습니다.
이제부터는 영어입니다.
On the current status of nuclear power generation, so much as advancements and disadvantages integrated by allsinfo nuclear power generation, etc
Hello, I am Alsinfo, who is publishing all the useful knowledge in the world. I will explain as briefly as possible the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power generation, which are power generation methods that utilize nuclear power, the most realistic, economical and useful energy source that Korea can choose.
I'm starting with the hope that it will help.
Nuclear Power: Choosing for a Sustainable Future
Nuclear power generation is a hot topic of debate in our society. Some argue that nuclear power is an environmentally friendly and sustainable energy source, while others raise concerns about safety and the disposal of radioactive waste. In this article, I would like to look at the pros and cons of nuclear power generation from a balanced perspective, and explore its role and future in depth.
1. advantages of nuclear power generation
1.1. Reducing carbon emissions and responding to climate change
Nuclear power has very low greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel power generation, which can contribute to the response to climate change. This is being seen as an important solution for sustainable energy supply.
1.2. Stable power supply
Nuclear power generation has high fuel supply stability, which is essential to industrial development and the national economy.
1.3. Economic feasibility
Nuclear power is considered to be more economical than fossil fuel power in the long run. Initial construction costs are high, but operating and fuel costs are low, resulting in low power generation costs.
2. the disadvantages of nuclear power generation
2.1. Disposal of radioactive waste
Radioactive waste generated during nuclear power generation has a problem that must be safely managed for a long time. It is an urgent task to come up with a solution.
2.2. Safety concerns
Safety concerns are high due to the risks and potential damage of nuclear power plant accidents. A thorough safety management system is needed.
2.3. Decreasing public acceptance
Public acceptance is decreasing due to the spread of negative perceptions about nuclear power generation. Efforts are required to overcome this.
3. the future of nuclear power generation
3.1. Strengthen technological innovation and safety
Recently, new nuclear power technologies such as small modular reactors and fourth-generation reactors are being developed. It is expected that safety and economic feasibility will be greatly improved.
3.2. Advances in radioactive waste management technology
Radioactive waste management technologies such as wick layer disposal and nuclear fuel recycling are continuously developing. Through this, it seems that we can find a clue to solving the waste problem.
3.3. Efforts to improve public acceptance
The government and industry are actively promoting the safety and necessity of nuclear power generation and making efforts to improve public acceptance by establishing a resident participatory decision-making system.
3.4. Re-establishment of the role of nuclear power generation
Based on technological advances and social consensus, the role of nuclear power generation is expected to be redefined. It could be established as a major means of achieving carbon neutrality.
conclusion
Nuclear power is one of the key options for a sustainable future. Nuclear power will be a key tool for achieving carbon neutrality if technological innovation and social consensus are used to increase safety and public acceptance, and address radioactive waste management issues. The government, industry, and civil society must work together to achieve this.
3. the future of nuclear power generation
3.1. Strengthen technological innovation and safety
Recently, new nuclear power technologies such as small modular reactors and fourth-generation reactors are being developed. It is expected that safety and economic feasibility will be greatly improved.
3.2. Advances in radioactive waste management technology
Radioactive waste management technologies such as wick layer disposal and nuclear fuel recycling are continuously developing. Through this, it seems that we can find a clue to solving the waste problem.
3.3. Efforts to improve public acceptance
The government and industry are actively promoting the safety and necessity of nuclear power generation and making efforts to improve public acceptance by establishing a resident participatory decision-making system.
3.4. Re-establishment of the role of nuclear power generation
Based on technological advances and social consensus, the role of nuclear power generation is expected to be redefined. It could be established as a major means of achieving carbon neutrality.
conclusion
Nuclear power is one of the key options for a sustainable future. Nuclear power will be a key tool for achieving carbon neutrality if technological innovation and social consensus are used to increase safety and public acceptance, and address radioactive waste management issues. The government, industry, and civil society must work together to achieve this.
5. Conclusion
Nuclear power generation will be able to establish itself as a sustainable future energy source through technological innovation and social consensus.
First, it is expected that the economic feasibility and safety of nuclear power generation will be greatly improved by the development of new reactor technology and the strengthening of safety. In addition, the development of radioactive waste management technology will be able to find a solution to this problem.
Second, active efforts by the government and industry will enhance public understanding of the necessity and safety of nuclear power generation and public acceptance. Social consensus can be reached through the establishment of a resident-participating decision-making system.
Third, the role of nuclear power will be redefined based on these technological and social advances. It will be able to contribute to the realization of a sustainable future by establishing itself as a key tool for achieving carbon neutrality.
The government, industry, and civil society should work together to achieve this. Technological innovation and institutional improvement should be continuously promoted based on social consensus on the safety and necessity of nuclear power generation.
What is the status of domestic development?
Status of nuclear power plant ownership:
Korea is the world's sixth-largest nuclear power generation country, operating 24 nuclear power plants.
About 30% of the total power generation is covered by nuclear power generation.
Government policy direction:
The government plans to increase the share of nuclear power to achieve its carbon neutrality target in 2050.
We are striving to develop next-generation nuclear reactors and strengthen safety.
Technology development and safety enhancements:
New nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors and fourth-generation reactors are being developed.
This is expected to greatly improve safety and economic feasibility.
Radioactive waste management:
Radioactive waste management technologies such as wick layer disposal and nuclear fuel recycling are developing.
Through this, it seems that we can find a clue to solving the waste problem.
Increase public acceptance:
The government and industry are actively promoting the safety and necessity of nuclear power generation.
We are striving to improve public acceptance by establishing a resident participatory decision-making system.
In summary, South Korea plans to use nuclear power as a major means of achieving carbon neutrality, and strives to increase the sustainability of nuclear power generation through technological innovation and social consensus enhancement.
the opening of a nuclear power plant
Currently, there are a total of 24 nuclear power plants in operation in Korea. These 24 nuclear power plants are located on the following six power plant sites:
Kori Nuclear Power Plant (Busan)
Hanbit Nuclear Power Plant (Glory of Jeollanam-do)
Hanul Nuclear Power Plant (Uljin, Gyeongbuk)
Wolseong Nuclear Power Plant (Gyeongju, North Gyeongsang Province)
Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (Daejeon)
Shin-Kori Nuclear Power Plant (Busan)
Among them, Gori, Hanbit, Hanul, and Wolseong nuclear power plants are the sites of major nuclear power plants. In addition, additional Shin-Kori nuclear power plants have been built and operated recently.
Therefore, it can be seen that 24 nuclear power plants are currently in operation at a total of 6 nuclear power plant sites in Korea.
This is the end of the preparation, and the author was ALLSINFO



